Description: Cell-free circulating (CFC) DNA/RNA and other cellular nanoparticulates are being increasingly studied for their potential as biomarkers for early detection of cancer and other diseases. In prior work, we developed a novel dielectrophoretic (DEP) method that allows the isolation and detection of DNA nanoparticulates directly from whole blood on a microarray device. We demonstrated the separation of high molecular weight (HMW) DNA and fluorescent particles in the 40 nm to 200 nm range from whole blood. Using the same microelectrode array and technique, we observed visible quantities of SYBR Green fluorescent-stained DNA in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) patient blood samples. New microarray devices have now been constructed that increase the ability to collect nanoparticulate material as well as allow the integration of the temperature control necessary to perform PCR thermal cycles. With the sample collection and analysis conducted in the same fluidic device, we have eliminated the need for any off-chip processing and created a truly seamless "sample-to-answer" diagnostic device for CFC-DNA based early disease diagnostics.
Downloads:
Contact: Avery Sonnenberg
Description: My project is DEP and EP device for separation and nanoparticle deposition by electorophoresis depositon (EPD). I made the chip for nanoparticle deposition, self assembly. Also the pipette device is designed for small biomoleculer collection and seperation. Read More →
Downloads:
PDF: [ 1 ]
Contact: Youngjun Song
Description: Enzymes are able to catalyze the transformation of all other biomolecules, providing the dynamics and very essence of life. Over the past three decades considerable efforts have been made to create synthetic versions of enzymes with are sometimes called synzymes. Most have failed, and the few so-called successes are at best only marginal exhibiting properties that can barely be described as catalytic. In our lab, series of amino acids are used to recreate the reaction site of proteases which utilizes hydroxyl, sulfhydral, imadazole and carboxyl groups. The cleavage reaction performed by Cys-His combination is studied through the addition of substrates p-nitrophenol acetate and acetic anhydride. The acetylation and the deacylation kinetics are studied through molecular modeling, UV spectrophotometry and NMR.
Downloads:
JPEG: [ 1 ]
Contact: Tsukasa Takahashi
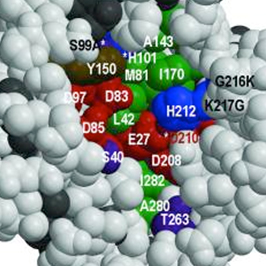
Description: Proteases are enzymes that hydrolyze peptide bonds. Elevated levels of proteases in the blood have been associated with several diseases such as shock, several types of cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and several others. Measuring the activity of this proteases is thus of importance in the development of new diagnostic techniques to many disorders.
In the lab we have develop multiple charge changing synthetic substrates for several proteases (trypsin, chymotrypsin, thrombin, MMP2/5 and elastase). They all allow us to detect protease activity directly in blood without any sample preparation by just lettiimages the sample react with out substrate, and then separating the products in an electrophoretic gel (see figure below). We are currently trying to develop a true point of care hand held device that can rapidly measure protease activity in directly in blood.
Downloads:
PowerPoint: [ 1 ]
Contact: Augusta Modestino
Coming Soon!

